Electric Vehicle
Electric Vehicle - Definition
An electric motor powers an electric vehicle (EV) as opposed to an internal combustion engine, which produces power by burning a mixture of fuel and gases. Therefore, in order to solve issues such as increased pollution, global warming, the depletion of natural resources, etc., such a vehicle is considered as a potential substitute for current-generation automobiles. Even though the idea of electric cars has been around for a while, it has attracted a lot of attention in the last ten years due to the growing carbon footprint and other environmental effects of fuel-powered cars.
Electric vehicles – Future of automobile
Due to their extremely low to zero carbon emissions, low noise, great efficiency, and flexibility in grid operation and integration, electric vehicles (EVs) are a viable technology for establishing a sustainable transportation sector in the future. An overview of electric vehicle technology, together with related energy storage systems and charging infrastructure, is provided in this chapter. The many electric-drive car kinds are displayed. Fuel cell electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, and battery electric vehicles are some examples. Each category's topologies and enabling technologies are addressed. New battery technologies, charger converter topologies, and power train configurations with various power trains are all introduced.
Types of electric vehicles
There are four different kinds of electric cars on the market:
Fully electric vehicle: a battery electric vehicle (BEV). When compared to hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles, these are more efficient.
Electric hybrid vehicles:
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): The car combines a battery-powered motor with an internal combustion (often petrol) engine. When the battery is dead, the petrol engine is used to both propel and charge the vehicle. Compared to completely electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles, these cars are less efficient.
Uses both an internal combustion engine and a battery that is charged from an external outlet. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) (they have a plug). This implies that electricity, rather than the vehicle's engine, can be used to recharge the battery. While less efficient than BEVs, PHEVs are more efficient than HEVs.
Electricity is created from chemical energy in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). Consider an FCEV powered by hydrogen.
Battery-powered automobiles (BEVs)
BEVs are also referred to as all-electric cars (AEV). Electric drivetrains driven solely by batteries are used in BEV-based electric vehicles. The enormous battery pack that houses the electricity needed to power the car may be charged by hooking it into the power grid. One or more electric motors are then powered by the fully charged battery pack to drive the electric vehicle. Click below to learn more about BEVs.
HEV (hybrid-electric vehicle):
HEVs are also referred to as parallel or series hybrids. HEVs have an electric generator in addition to an engine. Fuel powers the engine, while batteries provide electricity for the motor. Both the engine and the electric motor turn the transmission at the same time. Wheels are then propelled by this. Click below to learn more about HEVs.
PHEV: Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
The term "series hybrid" also applies to PHEVs. Both an engine and a motor are present. You have a choice of two types of fuels: conventional fuel (like gasoline) and alternative fuel (such as bio-diesel). A battery pack that can be recharged can also power it. The battery can receive external charging. Click the link below to learn more about PHEVs.
FCEVs: Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
Another name for FCEVs is zero-emission vehicles. To create the electricity needed to power the car, they use "fuel cell technology." The fuel's chemical energy is instantly transformed into electric energy. Click the link below to learn more about FCEVs.
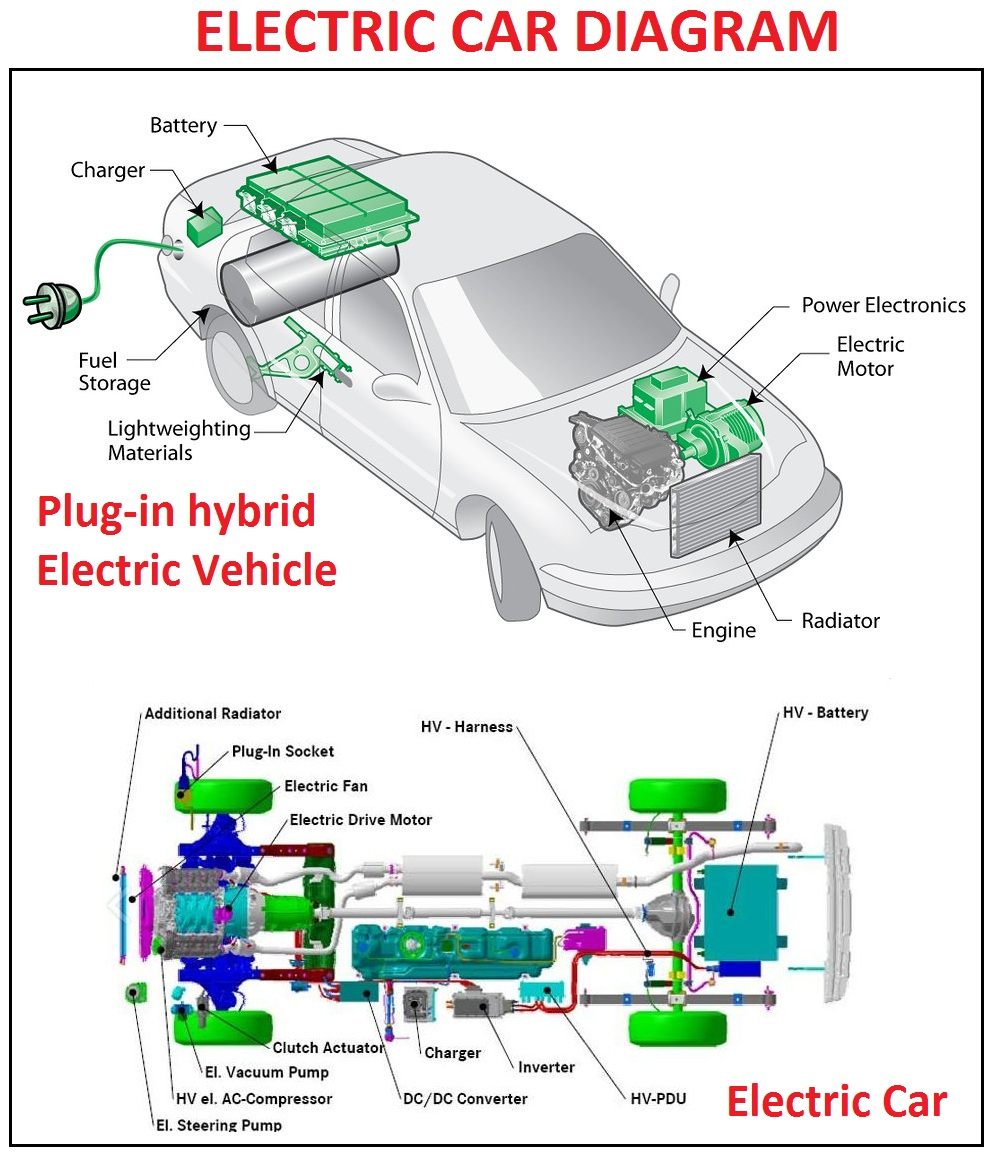
Operation of electric vehicle
An electric motor replaces the internal combustion engine in all-electric vehicles, often known as battery electric vehicles (BEVs). The electric motor of the vehicle is powered by a sizable traction battery pack, which must be hooked into a wall outlet or charging apparatus, also known as electric automobile supply apparatus (EVSE). The car does not have a tailpipe or any usual liquid fuel components like a fuel tank, fuel line, or fuel pump because it is an electric vehicle.
Major All-Electric Car Battery (All-Electric Auxiliary) Components: The auxiliary battery powers the car's accessories in an electric drive vehicle.
Charge port: The vehicle can attach to an external power source using the charge port to recharge the traction battery pack.
This device, known as a DC/DC converter, transforms higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack into the lower-voltage DC power required to operate the vehicle's accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Electric traction motor: This motor powers the wheels of the vehicle by drawing energy from the traction battery pack. Some automobiles employ motor generators that serve as both drives and regenerators.
The onboard charger transforms the incoming AC power from the charge port to DC power to charge the traction battery. While the pack is being charged, it also communicates with the charging apparatus and keeps track of battery properties including voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge.
The power electronics controller regulates the flow of electrical energy from the traction battery, regulating the torque and speed of the electric traction motor.
Thermal system (cooling): This system keeps the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components within a safe operating temperature range.
Electricity is stored in the traction battery pack, which the electric traction motor will utilize.
Electric transmission: The electric traction motor drives the wheels by transferring mechanical energy through the transmission.
Global scenario of electric vehicle
The market for electric cars is one of the most active in the clean energy sector. In 2021, the number of electric vehicle (EV) sales doubled from the previous year to reach a new high of 6.6 million. Only 120 000 electric vehicles were sold globally in 2012. More than that many will be sold each week in 2021. In 2021, the market share for electric vehicles was about 10% worldwide, up from just 2% in 2019. With this, there are now over 16.5 million electric vehicles on the road worldwide, which is three times more than there were in 2018. With 2 million electric vehicle sales in the first quarter of 2022, a 75% increase over the same time in 2021, the market for electric vehicles has continued to grow rapidly.