Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy- what is it?
The Greek words geo mean earth and therme are the sources of the word geothermal (heat). Geothermal energy is hence heat that originates from the earth. Buildings can be heated or electricity can be made using the steam and hot water that the earth produces. Because heat is continuously produced inside the earth and the water is replaced by rainfall, geothermal energy is a renewable energy source.
Energy of the earth
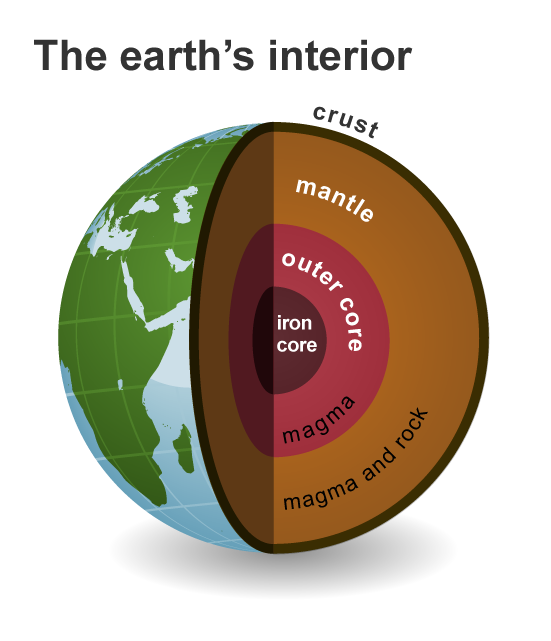
About 4,000 miles below the surface of the globe, in the earth's core, geothermal energy is produced. The inside of the sun continuously produces temperatures that are hotter than the surface of all rocks and undergo the slow radioactive particle decay that causes the earth. There are several distinct layers on the earth:
A solid iron core and an outer core consisting of extremely hot, molten rock, or lava, make up the core itself.
The roughly 1,800-mile-thick mantle encircles the core. Magma and rock make up its composition.
The crust, the layer of the earth that produces the landmass and ocean floors, is its topmost layer.
The plates that make up the earth's crust are divided. Near the borders of these plates, magma is close to the earth's surface. The location of volcanoes. Volcanoes spew out lava, some of which contains magma. The warmth from this magma is absorbed by the water and rocks deep underground. As you go further below ground, the water and rocks become hotter and hotter.
By drilling deep wells and pumping heated subsurface water or steam to the surface, people use geothermal energy to heat their houses and generate power. Alternatively, we can use the constant soil surface temperature to warm and cool structures.
Source of geothermal energy
Volcanoes, fumaroles (holes where volcanic gases are emitted), hot springs, and geysers are examples of geothermal energy that can occasionally reach the surface.
The most productive geothermal resources are typically found around significant plate borders where there are many earthquakes and volcanoes. The Ring of Fire is where the majority of the world's geothermal activity takes place. The Pacific Ocean borders this area.
When magma approaches the surface, it heats groundwater that is trapped in porous rock or water that is flowing over the surfaces and fissures of the cracked rock. These hydrothermal resources share two elements: heat and water. Geothermal reservoirs are naturally occurring, sizable areas of hydrothermal resources.
Geologists search for geothermal reservoirs in a variety of ways. The only method to confirm that a geothermal reservoir actually exists is to drill a well and measure the temperature very deep beneath.
Alaska, Hawaii, and the western states of the United States contain the majority of the country's geothermal reservoirs. The state that produces the most electricity from geothermal energy is California. The largest known dry steam field in the world is the Geysers dry steam reservoir in northern California.
Certain uses of geothermal energy
While some geothermal energy uses involve drilling kilometres into the earth, others make use of temperatures close to the surface. Geothermal energy is mostly used for three purposes:
1) Systems that utilize the hot water from nearby springs or reservoirs for direct usage and district heating.
2) A power plant needs water or steam that is extremely hot (between 300 and 700 degrees Fahrenheit). Where geothermal reservoirs are found within a mile or two of the surface, geothermal power plants are typically erected.
3) Geothermal heat pumps regulate the temperature of buildings above ground by using stable ground or water temperatures close to the earth's surface.
Procedure of geothermal energy production
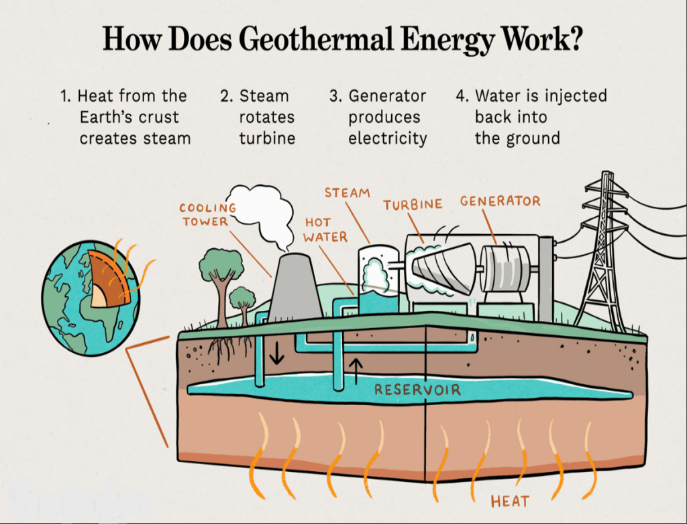
A well is drilled
A known geothermal reservoir has a production well drilled into it. In order to return used geothermal fluids to the geothermal reservoir, an injection well is typically also dug. Pipes transport hot geothermal fluids to a power plant where they are used to produce electricity.
The turbine is turned by the steam
The turbine blades on a shaft are turned by allowing pressurized geothermal fluid—or a secondary working fluid—to expand quickly and provide rotational or mechanical energy.
The electric generator is driven by the turbine
Direct use of the rotational energy from the rotating turbine shaft generates electrical current by spinning magnets inside a big coil. The main machinery for converting geothermal energy into electrical energy is the turbine and generator.
Transmission- Electricity is delivered by power lines
An external step-up transformer receives electrical current from the generator. Electrical current is delivered to homes, schools, and businesses via power lines after the transformer's voltage is raised.
The prospects of geothermal energy
Geothermal energy has the potential to significantly contribute to the development of a cleaner, more sustainable energy system in the United States and other parts of the world. It is one of the few renewable energy technologies that can deliver continuous, baseload power. Binary geothermal facilities can also be utilised as a flexible source of energy to offset the erratic supply of renewable resources like wind and solar, unlike coal and nuclear plants. Binary plants have the flexibility to ramp production up and down numerous times per day, from 100 percent of potential power down to a minimum of 10 percent.
Geothermal facility electricity prices are likewise getting more and more competitive. The levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for new geothermal plants, which are expected to go online in 2019, is expected to be less than 5 cents per kilowatt hour (kWh), as contrasted to more than 6 cents for latest natural gas plants and more than 9 cents for new standard coal plants, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). The direct use of geothermal resources as a source of heating for residences and establishments in any area also has a promising future.
However, in order to fully utilize geothermal energy, two cutting-edge technologies—Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) and co-production of geothermal electricity in oil and gas wells—need to be developed. Geothermal energy has a strong potential for meeting world’s energy demand in the future.